Summary
- Creatine is one of the most well-researched supplements. It benefits muscles, the brain, the heart, and overall health.
- It enhances ATP production, supporting strength, endurance, cognitive function, and recovery.
- Recent research suggests that higher doses (8-10g/day) may be needed for optimal cognitive benefits.
- Myths about creatine causing dehydration, kidney damage, and bloating are primarily debunked.
- It plays a role in surgical recovery by preserving muscle mass, reducing inflammation, and accelerating return to function.
- Most people—especially aging adults, vegetarians, and active individuals—should consider taking creatine, but some populations may need caution.
Reminder:
An excerpt follows, but the full post and an audio version are only available to subscribers.

Creatine and Brain Health
Creatine isn’t just for muscles—it’s essential for brain energy metabolism, cognitive function, and even mental resilience.
- The brain is an energy-intensive organ, relying on ATP for synaptic function, neurotransmitter balance, and neuroprotection.
- Creatine supports cognitive performance, particularly under conditions of stress, sleep deprivation, and aging.
- Studies show it may enhance memory, processing speed, and executive function, particularly in older adults and vegetarians, who tend to have lower creatine stores.
- Neuroprotective effects: Emerging research suggests creatine may help in conditions like traumatic brain injury (TBI), Parkinson’s, and depression by reducing oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction.
Takeaway: Creatine isn’t just for athletes—it supports brain function, mental clarity, and long-term cognitive health.

Creatine and Cardiovascular Health
Creatine improves energy efficiency in the heart and may protect against cardiovascular disease.
- The heart is a high-energy-demand organ, and creatine plays a key role in supporting cardiac ATP production.
- Creatine helps buffer pH levels, reducing lactate buildup, which can be beneficial for endurance and cardiovascular efficiency.
- Some studies suggest it can lower homocysteine levels, a marker associated with cardiovascular risk.
- Potential benefits for heart failure patients: Research indicates creatine may improve left ventricular function in individuals with congestive heart failure.
Takeaway: Creatine may support heart function, improve endurance, and contribute to cardiovascular health.
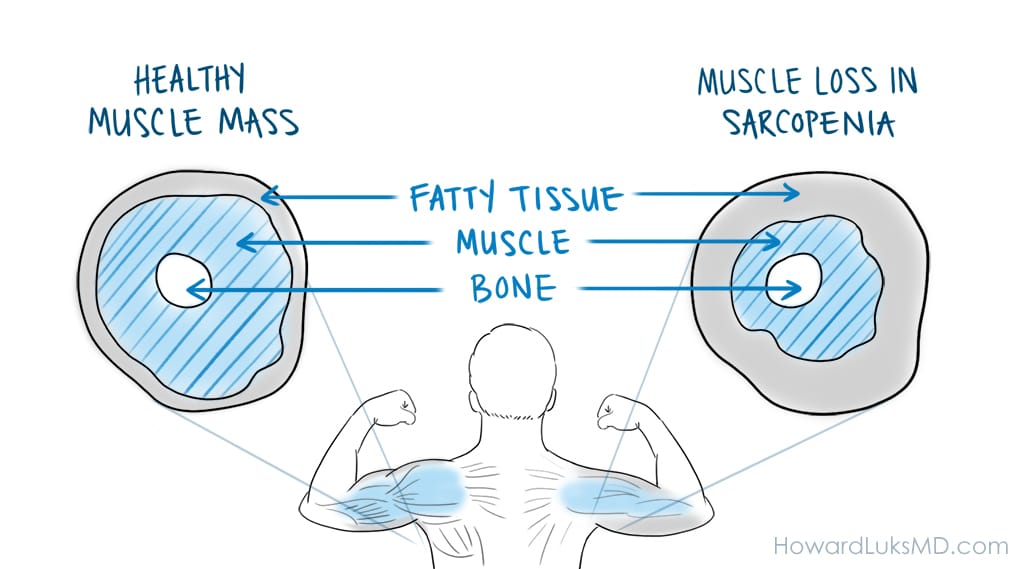
Muscle Mass, Strength, and Recovery
Creatine enhances strength, power, and recovery by (among other things) increasing ATP availability and reducing muscle breakdown.
- Boosts ATP production: More ATP means better strength, endurance, and performance.
- Improves muscle hydration and protein synthesis, promoting faster muscle recovery after training or injury.
- Reduces inflammation and muscle damage, which accelerates post-workout and post-surgical healing.
- Particularly important for aging adults, as creatine helps counteract sarcopenia (age-related muscle loss).
The balance of this post, including dosage, cautions, regimens, and an audio version of the post, is available to members only.
Audio Version (Members only)
Read the full article
Sign up now to read the full article and get access to all articles for paying subscribers only.
Already have an account?
Sign in